Early-Onset Arthritis: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
Dec 03, 2023 By Madison Evans
Early-onset Arthritis is a form of Arthritis that affects younger individuals than what is typically seen in the general population. This condition can cause debilitating pain, stiffness, and joint swelling in those affected. But with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can reduce their symptoms and gain more control over their health.
In this blog post, we will dive into early-onset Arthritis, including types of this condition, common symptoms to look out for, and approaches towards relieving the effects of early-onset Arthritis.
Learn how to spot the signs of early-onset arthritic and what steps you can take to receive supportive patient care for your future well-being.
Early-Onset Arthritis

Early-onset Arthritis is a form of joint disease that can manifest at an earlier age than what's
typically seen in the general population. Osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and lupus are all considered early-onset when they occur before age 50, 30, or 15, respectively.
Additionally, juvenile arthritis cases are also classed as early-onset due to the autoimmune nature of the condition.
The good news is that early diagnosis and treatment can help minimize symptoms and give those affected a better quality of life. If you or someone you know shows signs of Arthritis, you must speak to a doctor immediately for further diagnosis and management. With the right care, early-onset Arthritis can be controlled and managed effectively.
Types of Early-Onset Arthritis
Similar to arthritis, early-onset diseases arthritis is a catch-all term for a variety of the disease's manifestations. The following are examples of early-onset arthritis:
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease that can affect people of any age, although it is more commonly seen in those aged 30-50.
RA presents itself in several ways, including explosively in one or two days or as a palindromic presentation with joint swelling involving a few joints before spreading to others.
Common symptoms include stiffness, pain in movement, tenderness, and fatigue. Malaise may occur weeks before other symptoms arise, and low-grade fever can also be present.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage the condition and reduce its effects on the individual's life. With proper care, individuals with early-onset RA can gain greater control over their health and lessen the condition's debilitating effects.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of Arthritis. It usually starts in individuals over 50 but can occur at any age - making it an early-onset condition.
Symptoms of OA may start gradually and worsen over time, such as aching joints, joint stiffness in the morning or after resting, limited range of motion that may go away with movement, clicking or cracking sounds when a joint bends, swelling around a joint, muscle weakness around a joint, and unstable joints like if your knee gives out.
It is important to pay attention to these symptoms to properly treat them to maintain quality of life and manage pain levels.
Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic Arthritis is a type of early-onset Arthritis that occurs in those who have psoriasis, a skin disorder. This condition typically appears 10 to 20 years after psoriasis symptoms begin; however, some people may experience joint pain before skin lesions appear.
Generally, people are between 30 and 40 when they develop psoriatic Arthritis. Symptoms of this condition include pain and swelling in the joints, stiffness, fatigue, and patches of psoriasis covering many body areas.
Episodes can become worse over time before improving again. To manage these episodes, individuals should consult their doctor about diagnostic testing or treatment options to reduce their symptoms and gain more control over their health.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is an inflammatory form of early-onset Arthritis often characterized by severe chronic pain and stiffness, primarily in the lower back and buttocks. The onset usually occurs between ages 17 to 45, though it may be considered early onset in young adults before age 17.
Symptoms can include frequent pain and stiffness, mild fever, loss of appetite, mild to moderate anemia, bowel inflammation, and uveitis. Over time, the symptoms may worsen with increased pain and stiffness lasting at least three months.
Pain may extend up the spine into the neck area and to other parts of the body, such as thighs, shoulder blades, hips, ribs, and heels. Proper diagnosis and treatment of AS can help reduce symptoms and give individuals more health control.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune condition of the body's connective tissues. It most commonly affects people between 15 and 45 years of age, making it an early-onset form of Arthritis.
Common signs and symptoms include a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, mouth sores, hair loss, chest pain, joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Diagnosis is made through physical exams, lab tests, and imaging tests such as x-rays or MRI scans.
Treatment typically includes medications to reduce inflammation or suppress the immune system and lifestyle modifications to reduce stress and improve overall health.
Juvenile Arthritis
Juvenile Arthritis is a type of early-onset Arthritis that affects children between 6 months and 16 years old.
High fevers that often peak in the evening and then abruptly subside, limping or hurting wrists, fingers, or knees, rash appearances and disappearances, rigidity in the neck, hips, or other joints, and unexpected swelling of the joints that persist as enlargements are also common symptoms.
Though there is no cure for juvenile Arthritis, some children have achieved permanent remission with proper diagnosis and treatment. It's important to seek medical attention if your child exhibits any of the symptoms mentioned above, as it can help relieve their pain and improve their health.
Early-Onset Arthritis Symptoms
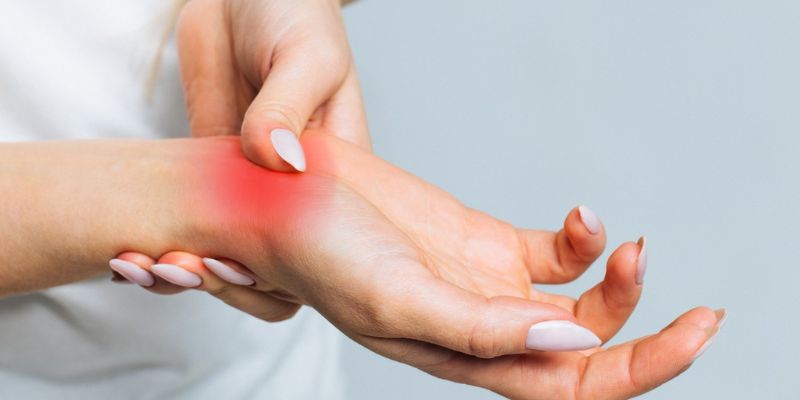
Early-onset arthritis symptoms can vary in intensity and duration. Some important symptoms are as follows:
- Pain is a common symptom of early-onset Arthritis, which may come and go or be more persistent in certain joints.
- Swelling
- Redness
- Warmth around the joint may also occur for three days or more or occur more than three times per month.
- Difficulty moving a joint may be experienced due to pain and stiffness.
Treatment
When it comes to treating early-onset Arthritis, several approaches can be taken. These include physical or occupational therapy, medications, surgery, and lifestyle changes.
Physical Therapy/Occupational Therapy
Physical and occupational therapists work with individuals to help reduce pain, improve strength and flexibility of the joints, increase independent ambulation (the ability to walk from place to place), and use assistive devices as needed. This therapy is important for helping people maintain their independence while managing their symptoms.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help reduce pain associated with early-onset Arthritis. Low doses of corticosteroids can help reduce joint inflammation during flare-ups.
Also, DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) can suppress the body's overactive immune system, often responsible for developing early-onset Arthritis.
Surgery
Some individuals with early-onset Arthritis may require surgery to repair ruptured tendons due to the inflammatory process. Surgery can also restore function in those whose joints have been affected by inflammation and joint damage.
Lifestyle Changes
Weight management is important in managing early-onset arthritis symptoms. Excess weight strains joints and organs, so losing or maintaining a healthy weight can reduce stress.
Proper diet and exercise can also help manage inflammation, improve mobility, and relieve pain.
FAQs
How can I tell what kind of Arthritis I have?
An accurate diagnosis can only be made by consulting your doctor. Your doctor may recommend blood tests, x-rays, ultrasounds, or other imaging to determine what type of Arthritis you have.
Is there a cure for early-onset Arthritis?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for early-onset Arthritis; however, proper treatment and lifestyle modifications can help reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Are there any natural remedies that can help manage my pain levels?
Yes! Natural remedies such as physical therapy, yoga, massage therapy, acupuncture, heat/cold therapy, and tai chi may help reduce inflammation and alleviate joint pain associated with early-onset Arthritis.
Conclusion
Early-onset Arthritis is a condition that affects younger individuals and can cause debilitating pain, stiffness, and joint swelling. The main types of early-onset Arthritis include ankylosing spondylitis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and juvenile Arthritis. Symptoms vary depending on the type of condition but can include pain, stiffness, swelling, and redness. With proper diagnosis and treatment from a doctor, individuals can reduce their symptoms and gain control over their health. Treatments may include lifestyle modifications, physical therapy, medications, or surgery.
-
 Oct 14, 2023
Oct 14, 2023Are Headaches a Sign of Stroke
Learn if headaches are a sign of stroke and why paying attention to your body is important. Get facts and tips on recognizing potential signs before they become serious health risks.
-
 Dec 18, 2023
Dec 18, 2023Benefits of Olive Oil for Your Skin
Learn how to use olive oil to nourish and protect your skin from the outside. Discover the many benefits of this natural, nutrient-rich ingredient and how it can help promote healthier-looking skin!
-
 Jan 13, 2024
Jan 13, 2024Wrist Tendonitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Experiencing discomfort or pain in your wrist? Learn more about the causes and symptoms of wrist tendonitis and treatment options available to care for it.
-
 Feb 19, 2024
Feb 19, 2024What Is Carboxytherapy
Learn what carboxytherapy is, how it works, and its potential to offer natural results without discomfort or downtime. Find out how this innovative beauty trend can help minimize signs of aging while improving overall skin tone.
