What Is Reactive Airway Disease
Dec 08, 2023 By Madison Evans
Are you having trouble breathing? You may have reactive airway disease, which affects the respiratory system and can cause difficulty breathing. Reactive airway disease often has similar symptoms to asthma, such as wheezing or coughing, making it hard to diagnose correctly.
In this blog post, we'll explore reactive airway disease in more detail - what causes it, how it's diagnosed and treated, and more. Keep reading to learn about one of the most common lung conditions affecting children and adults alike!
What Is Reactive Airway Disease
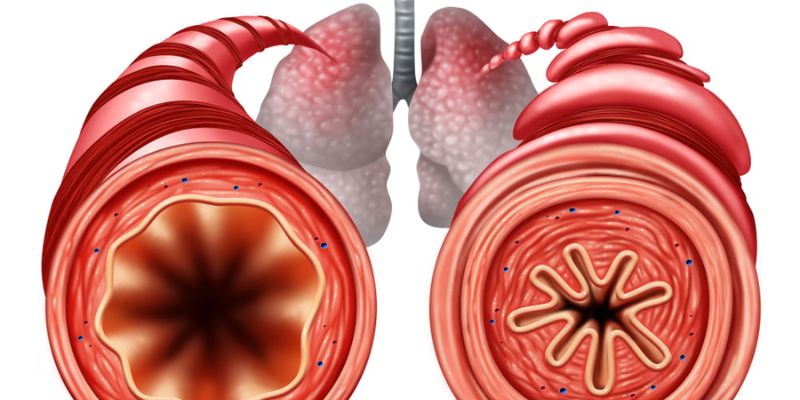
Reactive airway disease, or RAD, is a lung condition in which bronchial tubes overreach to reactants that affect the respiratory system. It is marked by difficulty breathing and is often mistaken for asthma due to similar symptoms.
Symptoms Of Reactive Arway Disease
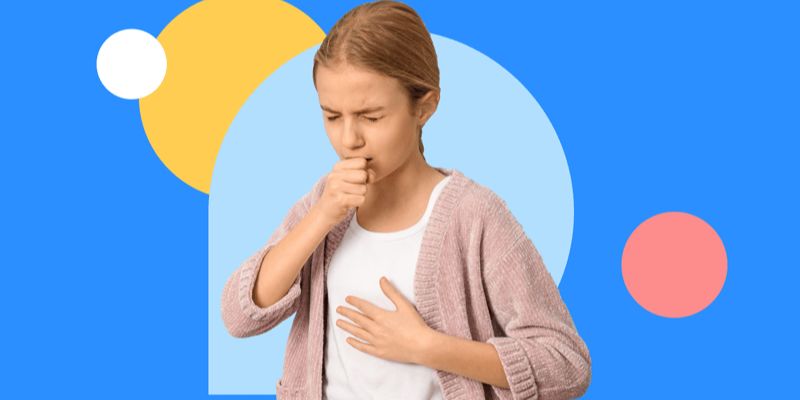

Reactive airway disease (RAD) is a chronic lung condition affecting the respiratory system, making breathing difficult. It often has symptoms similar to asthma and can be difficult to diagnose correctly. Common symptoms include the following:
Chronic Cough That Clears Mucus (Sputum)
One of the most common symptoms of reactive airway disease is a persistent cough that produces sputum or mucus deep in your lungs. This cough usually occurs after you engage in physical activity or when exposed to certain airborne allergens such as pollen or dust mites. It is often productive, meaning it will produce sputum or mucus.
Shortness of Breath
Reactive airway disease can also cause shortness of breath. This is because the airways become narrowed due to inflammation, making it difficult to take a full breath without feeling an uncomfortable tightness in your chest. You may have difficulty catching your breath or need to take shallow breaths instead of deeper ones.
Difficulty Breathing
In addition to coughing and shortness of breath, reactive airway disease can make it hard for you to breathe properly. The narrowing of the airways makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass through them, resulting in a sensation of being unable to draw in a full breath.
This can lead to fatigue and difficulty exerting yourself during everyday activities, such as walking up stairs or brisk walking outside.
Wheezing
Wheezing is another common symptom of reactive airway disease. You may hear a whistling or squeaking sound when you breathe out due to the narrowing of your airways caused by inflammation. It's important to speak with your doctor if you experience this symptom so they can help diagnose and treat your condition correctly.
Chest Tightness
Finally, chest tightness is another symptom associated with reactive airway disease. The feeling of tightness in your chest occurs because the narrowing of the airways makes it harder for oxygen to pass through them easily. This can be uncomfortable and cause mild to moderate discomfort in your chest or even an ache that won't seem to go away.
What Causes Reactive Airway Disease
Many potential triggers can lead to reactive airway disease. These include:
- Allergies: If you're allergic to certain substances like dust mites, pollen, food, or pets, exposure to these allergens can trigger an inflammatory response in your lungs which leads to RAD.
- Bacterial infections: Bacterial lung infections can cause an overproduction of mucus, contributing to RAD.
- Viral infections: Common viruses such as influenza, adenovirus, and rhinoviruses can lead to airway inflammation and cause RAD.
- Chemical gases, perfumes, or fumes: Exposure to chemical irritants like cleaning products, smoke from cigarettes or other sources, and fragrances from perfumes or sprays can all lead to reactive airway disease.
- Smoke: Cigarette smoking is one of the most well-known triggers for RAD. It irritates the lungs and causes inflammation that makes it hard to breathe.
- Exercise: When you exercise vigorously, your breathing rate increases, and you breathe more air. This can cause the airways to constrict and lead to RAD symptoms.
- Cold air, hot air, humidity, or changes in the weather: These environmental factors can affect your lungs by causing a decrease in oxygen or an increase in allergens that trigger inflammation of the respiratory system.
These triggers are important to be aware of when identifying reactive airway disease. Depending on your circumstances, some may have a greater impact than others, so it's important to understand what is most likely causing your breathing problems before taking steps toward treatment.
How is Reactive Airway Disease Diagnosed
Reactive airway disease (RAD) is a common lung condition that can make breathing difficult. Getting an accurate diagnosis is important to provide the right treatment and manage your symptoms effectively.
Diagnosing RAD requires a physical examination, lab tests, imaging tests, and other specialized procedures. Here's what you need to know about each one:
- Physical Examination – During your physical exam, your doctor will look for signs of RAD, such as wheezing or coughing. They may also check your chest and abdomen for any tenderness or swelling.
- Spirometry – This test measures how much air you can inhale and exhale. It's usually performed in a doctor's office or hospital.
- Imaging Tests – X-rays and CT scans may be used to look for any lung abnormalities, such as narrowing of the airways.
- Blood Tests – A blood test can check for inflammation markers associated with RAD.
- Skin (scratch) Prick Test – This is often done to rule out allergies as the cause of RAD symptoms. A small amount of allergen is placed on the skin during this test and scratched lightly. If you have RAD, you should not experience any reaction from this test.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) – An ECG is a test that records the electrical activity of your heart. This helps determine if any underlying cardiac issues may be causing RAD symptoms.
- Pulse Oximetry – This test measures the oxygen level in your blood. Low levels of oxygen can be a sign of RAD.
- Exercise Testing – Exercise testing, also known as cardiopulmonary exercise testing, monitors how well your lungs and heart respond to physical activity and exertion. It's often used to diagnose RAD in athletes and those who engage in strenuous activities regularly.
How Reactive Airway Disease Is Treated
Several treatment options are available to manage the symptoms of RAD and improve quality of life.
Bronchodilators
One type of treatment used to help treat RAD is bronchodilators. Bronchodilators are medications that open the airways to make breathing easier.
They come in both inhalable and oral forms. Inhalable bronchodilators work quickly, but their effects only last for a short time – usually four or eight hours. Oral bronchodilators take longer to start working but their effects last for 12 or 24 hours.
Oxygen Therapy
In some cases, oxygen therapy may be recommended if the patient has difficulty breathing due to low oxygen levels. The patient is given supplemental oxygen through a mask or nasal cannula, which helps increase oxygen levels and improve breathing.
Oxygen therapy can help improve quality of life and reduce any associated symptoms with RAD, such as fatigue or shortness of breath.
Epinephrine Injection
Some patients with RAD may need an epinephrine injection to quickly stop an asthma attack or severe wheezing episode. Epinephrine is a medication that relaxes the muscles of the airways, making it easier to breathe.
Epinephrine injections are given in an emergency when other treatments fail to provide relief or if the patient has difficulty breathing.
Corticosteroids (Steroids)
Another type of treatment used for RAD is corticosteroids, which are medications taken orally or through inhalation. Corticosteroids help reduce inflammation in the airways and can help improve symptoms like wheezing and coughing. They may also be recommended as a maintenance therapy to prevent future episodes of RAD.
FAQs
How long can reactive airway disease last?
Reactive airway disease can last for weeks, months, or even years. Treatment plans should be tailored to the individual and their particular symptoms.
What is the best way to prevent reactive airway disease?
The best way to prevent RAD is by avoiding known triggers such as smoke, allergens, and chemical irritants. It's also important to get annual flu shots and avoid strenuous activity if you have RAD.
Does reactive airway disease go away?
Yes, RAD can go away with the right treatment and management. However, it may take some time for symptoms to improve.
Conclusion
Reactive airway disease is a long-term medical condition that can make breathing more difficult. It affects the bronchial tubes, leading to coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Allergies and asthma typically cause RAD but may also develop after a respiratory infection or lung injury. Its diagnosis involves a physical examination, lab tests, imaging studies, and specialized procedures. While there is no cure for RAD, proper treatment can help patients manage their symptoms and lead healthier lives.
-
 Jan 12, 2024
Jan 12, 2024What is Histamine Intolerance
Are you experiencing uncomfortable symptoms and don't know why? Learn about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods and treatment options for histamine intolerance. Find out more and get back to feeling your best!
-
 Oct 14, 2023
Oct 14, 2023What Is the Puréed Diet
Are you looking to explore a new diet? In this blog post, we'll dive into the details of what is a puréed diet alongside its nutritional considerations and alternative options. Learn more with us today!
-
 Dec 23, 2023
Dec 23, 2023What is Lecithin
Are you curious about lecithin and its potential health benefits? Discover lecithin, its use, and why people have been consuming it for centuries.
-
 Feb 05, 2024
Feb 05, 2024Does Eczema Go Away
Do you have eczema and are wondering if it will ever go away? Get all the facts about this common skin condition. Discover what treatments can help manage your symptoms.
